The Role of Artificial Intelligence in ESGs and UN’s SDGs

Introduction to AI, ESGs and SDG’s
In recent years, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors has gained significant attention across industries. AI and ESG are transformative forces shaping the future of business, investment, and society. This article provides an overview of AI and ESGs, highlighting their growing importance and the synergistic potential they offer.
ESGs derived from UN’s SDGs
The United Nations (UN) 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) consist of a global call to action to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity. They cover environmental sustainability, social inclusion and economic growth. There is also a focus on health, education, gender equality and climate action.
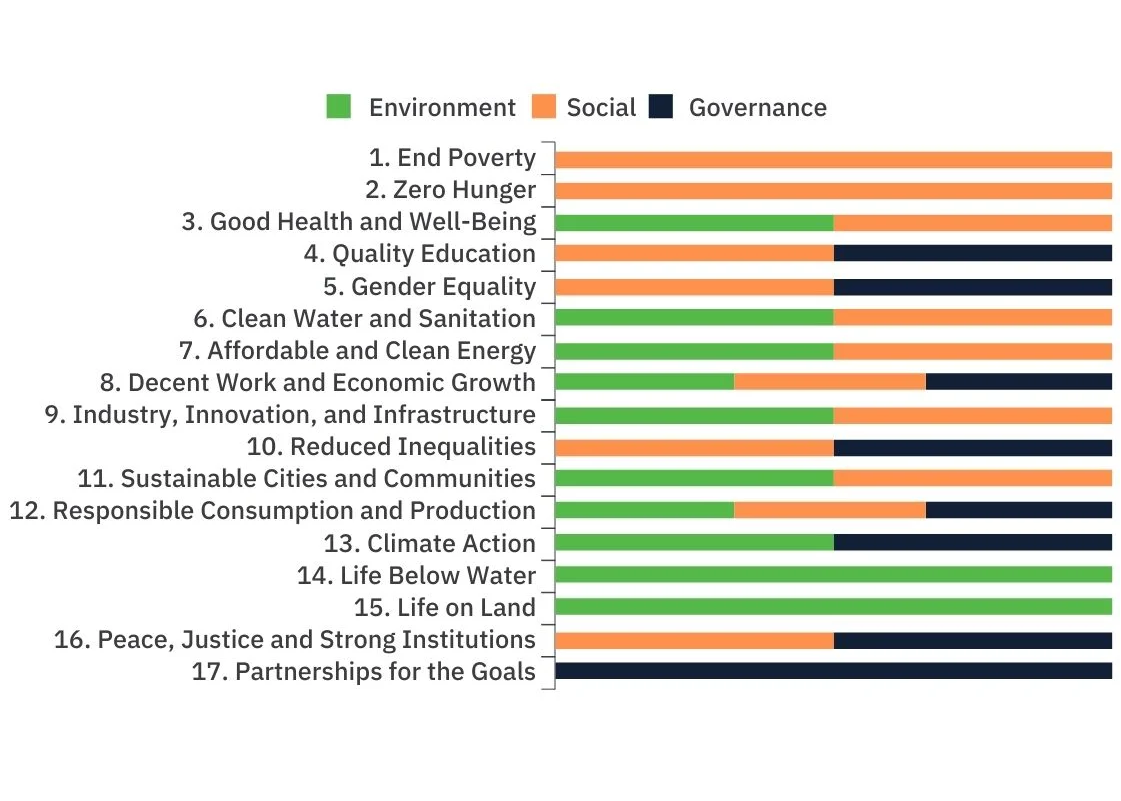
ESG framework helps achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). By incorporating ESG factors in the decision-making process, organizations significantly contribute to reaching Sustainable Development Goals. On the corporate side, ESG considerations can be broadly mapped to SDGs as shown below.
Relating ESG to UN’s 17 SDGs[1]
Understanding AI and ESGs
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. These intelligent systems can perform tasks such as recognizing speech, making decisions, translating languages, and analyzing data. AI technologies, including machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics, are revolutionizing various sectors by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and productivity.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors represent the three central dimensions for measuring the sustainability and ethical impact of an investment in a company or business. Environmental criteria consider how a company performs as a steward of nature, social criteria examine how it manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and communities, and governance deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights.
The Growing Importance of ESGs
In today’s business environment, ESG criteria are becoming increasingly important. Investors, consumers, and regulators are placing more emphasis on sustainability and ethical practices. Companies that prioritize ESG factors are often seen as more responsible, resilient, and better prepared for long-term success. This shift is driven by several factors:
- Investor Demand: Investors are seeking more than just financial returns; they want to invest in companies that align with their values and contribute positively to society. ESG investing, also known as sustainable or socially responsible investing, is rapidly growing, with significant capital flowing into ESG-focused funds.
- Regulatory Pressure: Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are implementing stricter regulations related to environmental protection, social responsibility, and corporate governance. Companies must comply with these regulations to avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Consumer Expectations: Modern consumers are more informed and conscious about the impact of their purchases. They prefer brands that demonstrate commitment to sustainability and ethical practices. This consumer preference drives companies to integrate ESG factors into their strategies.
The Role of AI in ESG Implementation
AI is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance the implementation and monitoring of ESG initiatives. By leveraging AI, businesses can:
- Analyze Large Data Sets: AI can process and analyze vast amounts of data at a speed and accuracy unattainable by humans. This capability is crucial for evaluating ESG performance, identifying trends, and making informed decisions.
- Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can predict future ESG risks and opportunities by analyzing historical data and current trends. This predictive capability helps companies proactively address potential issues and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- Automation: AI-driven automation can improve efficiency and reduce the environmental impact of operations. For example, AI can optimize energy usage in buildings, reduce waste in manufacturing processes, and enhance supply chain management.
- Enhanced Reporting: AI can streamline ESG reporting by automating data collection and analysis, ensuring accuracy, and providing real-time insights. This enhances transparency and accountability, which are critical for building trust with stakeholders.
Conclusion
The intersection of AI, ESG and SDGs represents a promising frontier for innovation and sustainability. As businesses and investors increasingly recognize the value of integrating AI with ESG/SDGs principles, we can expect to see more advanced solutions driving positive environmental and social outcomes. Embracing this synergy not only helps in addressing global challenges but also paves the way for sustainable and ethical growth in the future.
To learn to harness the power of AI to bring large and sustainable changes, check out our MTech Artificial Intelligence or MSc Business Analytics and the capstone projects.